Within the rapidly evolving landscape of Ethereum scaling, the OP Superchain stands out for its ambitious vision of unifying multiple rollups into a seamless, interoperable network. Yet, until recently, one of the most significant hurdles to this vision has been the lack of efficient cross-rollup composability. Each rollup traditionally operated with its own sequencer, resulting in fragmented liquidity and complex, asynchronous workflows for applications attempting to span more than one chain. This siloed approach undermined the very promise of a monolithic user experience that the Superchain aspires to deliver.

The Role of Shared Sequencers in Multi-Rollup Coordination
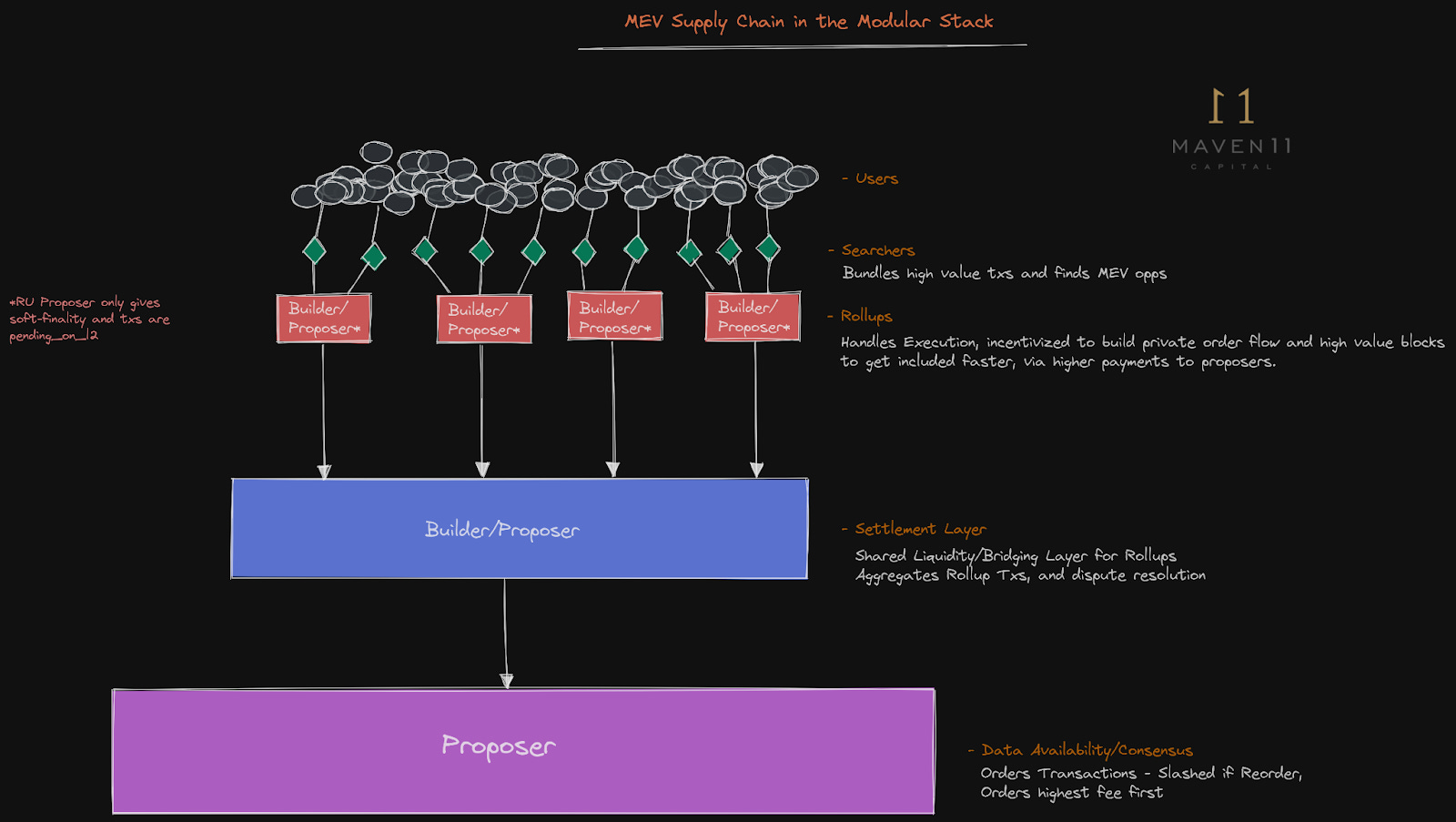
Enter shared sequencers – decentralized networks that coordinate transaction ordering and execution across multiple rollups. Among these, Espresso has emerged as a leading solution, offering a robust shared sequencing layer that enables atomicity and synchronous execution between participating chains. By integrating with a shared sequencer like Espresso, rollups within the OP Superchain can now achieve what is known as synchronous atomic composability: transactions that span several rollups either succeed or fail as one indivisible operation.
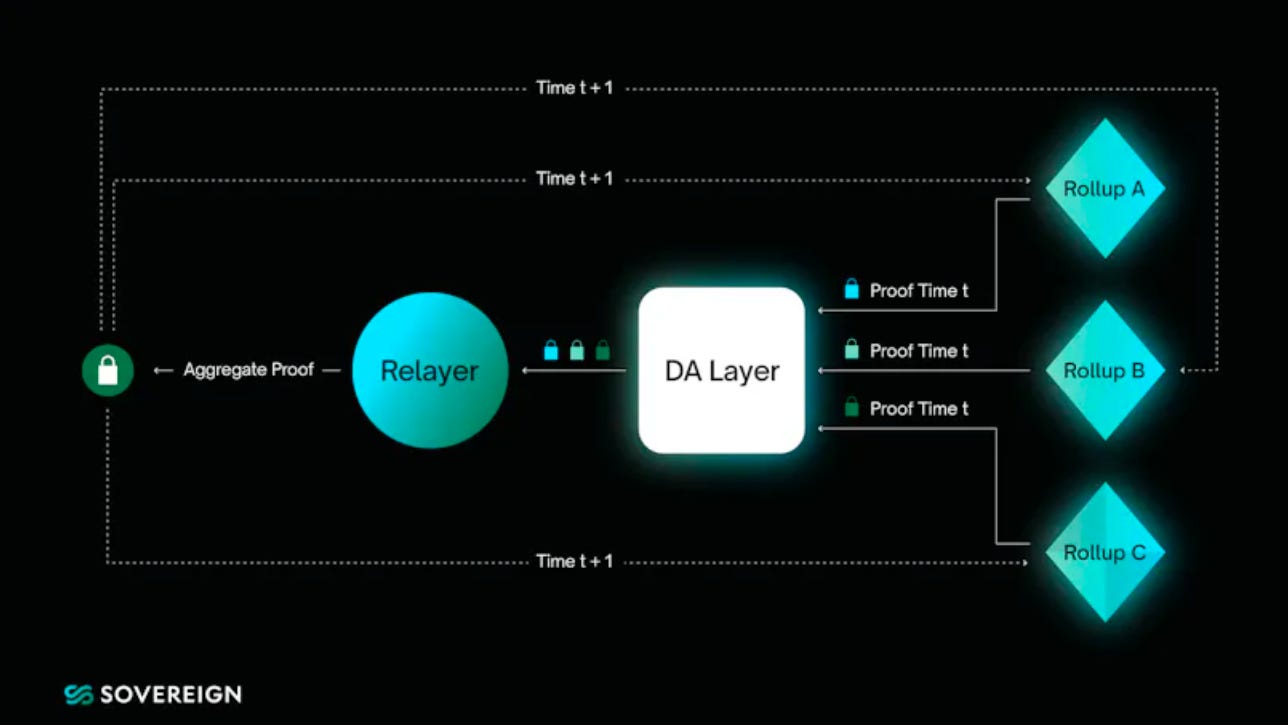
This capability is not merely academic. Consider cross-rollup decentralized exchanges (DEXs), where trades might require moving assets atomically between two different L2s. Without shared sequencing, users are exposed to race conditions and failed transactions if one leg executes while another does not. Espresso’s HotShot consensus protocol delivers fast confirmations and near-instant finality, dramatically reducing settlement risk and latency for these complex workflows.
How Espresso Powers Cross-Rollup Composability in the OP Superchain
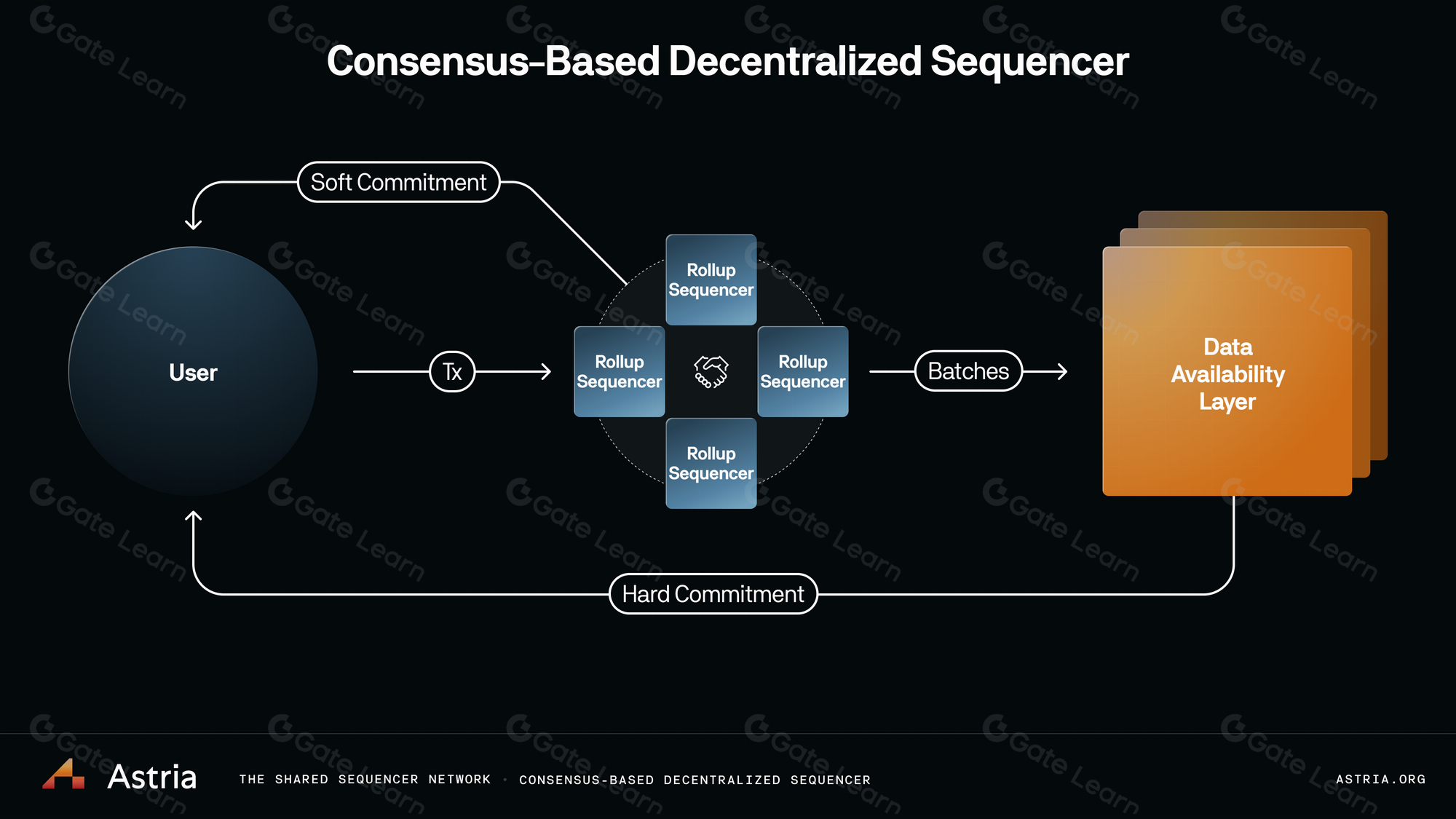
The technical foundation for this leap forward lies in Espresso’s decentralized sequencing architecture. Unlike legacy models where each rollup maintains its own isolated sequencer set, Espresso enables multiple chains to plug into a common coordination layer. This shared environment allows them to:
Key Benefits of Shared Sequencers Like Espresso for OP Superchain Developers
-
Atomic Cross-Rollup Transactions: Espresso enables atomic execution of transactions across multiple rollups within the OP Superchain, ensuring that complex operations either succeed or fail as a whole. This is critical for applications like cross-rollup DEXs, where transaction consistency is essential.
-

Synchronous Composability: By providing a shared sequencing layer, Espresso allows developers to build dApps that can interact across rollups in a synchronous and composable manner, greatly simplifying cross-chain logic and workflows.
-

Decentralized and Secure Sequencing: Espresso offers a decentralized sequencer network that reduces reliance on single rollup sequencers, enhancing security and censorship resistance for OP Superchain developers.
-

Near-Instant Finality with HotShot Consensus: Espresso’s HotShot consensus protocol delivers fast transaction confirmations and near-instant finality, improving the user experience by significantly reducing settlement times.
-
Unified Liquidity and Interoperability: By facilitating interoperability and liquidity unification across integrated rollups, Espresso helps OP Superchain developers tap into a broader user base and capital pool, as demonstrated by its collaboration with Polygon Labs on the AggLayer solution.
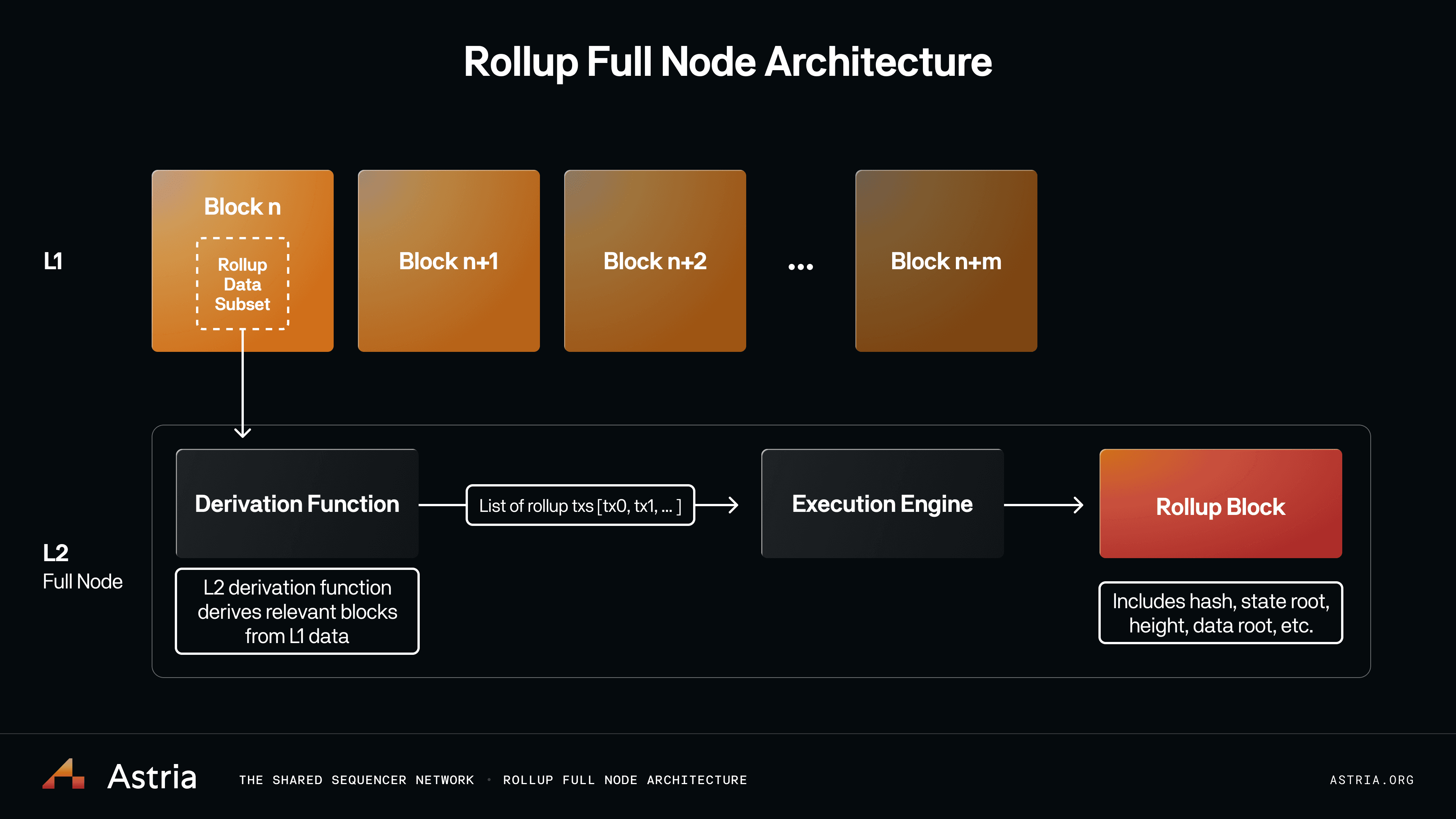
Espresso’s design ensures that all participating rollups observe the same ordering for cross-chain transactions within a block. This deterministic sequencing is essential for applications such as lending protocols or NFT marketplaces seeking to leverage liquidity and state across several L2s simultaneously.
The collaboration between Espresso and major ecosystem players extends beyond just technical integration. For instance, their partnership with Polygon Labs on AggLayer aims to further unify fragmented liquidity across Ethereum’s scaling stack by providing efficient coordination mechanisms and rapid transaction finalization (blockworks.co). These developments signal a broader industry movement toward modular scaling solutions that prioritize both security and user experience.
Synchronous Atomicity: The New Standard for Layer-2 Interoperability
Synchronous atomicity – guaranteed by systems like Espresso – is rapidly becoming an expected standard rather than an aspirational feature within the multi-rollup world. As highlighted in research from Delphi Digital and Optimism (docs.espressosys.com), enabling atomic cross-chain interactions is fundamental for unlocking new classes of decentralized applications previously constrained by inter-chain friction.
This paradigm shift also brings about important implications for protocol security and MEV mitigation. Decentralized sequencing reduces centralization risks inherent in single-sequencer designs while providing fairer transaction ordering mechanisms across all integrated rollups.
Furthermore, by synchronizing transaction ordering across multiple rollups, shared sequencers like Espresso help mitigate the risk of MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) exploitation and censorship. When a single entity controls sequencing, it becomes a potential point of failure or manipulation. Espresso’s decentralized approach distributes this power, enhancing both the security and neutrality of the entire OP Superchain ecosystem.
Developers building on the OP Superchain now have access to a composable infrastructure that was previously unattainable. This unlocks use cases such as cross-rollup lending, unified NFT marketplaces, and interoperable DeFi protocols that can tap into liquidity pools spanning several L2s. The result is a more vibrant, liquid, and resilient ecosystem where innovation is not stifled by technical fragmentation.
Practical Implications for Developers and Users
The operational improvements brought by shared sequencers are tangible at every layer of the stack. For developers, integrating with Espresso means:
Key Developer Benefits of Shared Sequencers in OP Superchain
-
Atomic Cross-Rollup Transactions: Shared sequencers like Espresso enable developers to build applications that execute transactions atomically across multiple rollups. This ensures that multi-rollup operations, such as cross-chain swaps or lending, either fully succeed or revert as a whole, greatly reducing risk and complexity.
-
Synchronous Composability: By providing synchronized transaction ordering, shared sequencers allow smart contracts on different OP Superchain rollups to interact in a single block. This enables new classes of dApps, such as cross-rollup DEXs and DeFi protocols, that require real-time composability.
-

Near-Instant Finality with HotShot Consensus: Espresso’s HotShot consensus protocol delivers fast confirmations and near-instant finality for cross-rollup transactions. Developers benefit from reduced settlement times, leading to smoother user experiences and more responsive applications.
-

Unified Liquidity Across Rollups: Integrating with a shared sequencer network helps unify fragmented liquidity pools across OP Superchain rollups. Developers can tap into deeper liquidity for their dApps, improving capital efficiency and enabling larger, more reliable trades.
-
Streamlined Interoperability and Scalability: Shared sequencers like Espresso, in collaboration with projects such as Polygon Labs’ AggLayer, offer developers a scalable and interoperable environment. This facilitates efficient coordination between rollups and supports the growth of complex, interconnected layer-2 ecosystems.
Users benefit as well. They experience faster confirmations, seamless asset transfers across rollups, and reduced settlement failures when interacting with multi-chain dApps. The user journey aligns more closely with the “monolithic” feel promised by the Superchain vision, without sacrificing decentralization or trustlessness.
Looking Ahead: Scaling Ethereum’s Interoperability Frontier
Espresso’s model is already influencing new design patterns across other scaling solutions. As more rollups adopt shared sequencing, whether through Espresso or alternative networks such as Astria or Radius, the Ethereum ecosystem inches closer to true synchronous composability at scale. These advances will be critical as demand for high-throughput applications continues to grow and as institutional players seek robust infrastructure for complex financial products.
Yet challenges remain. Ensuring liveness guarantees during network partitions, optimizing fee markets across chains, and maintaining robust decentralization in sequencer sets are all active areas of research and development. What is clear is that shared sequencers are no longer just an experimental concept, they are fast becoming foundational infrastructure for next-generation blockchain scalability.
For those tracking multi-rollup coordination, the rise of decentralized sequencing marks an inflection point in blockchain architecture. By abstracting away inter-chain complexity while preserving cryptographic security guarantees, solutions like Espresso are setting new standards for what developers and users can expect from layer-2 ecosystems.
The future of Ethereum scaling will be shaped not just by throughput or cost-efficiency but by how seamlessly independent rollups can interoperate without trust assumptions or operational bottlenecks.
The OP Superchain’s embrace of shared sequencers signals its commitment to this future, one where composability is native, liquidity is unified, and innovation flows unimpeded across every corner of the network.






